Introduction: Bus bar is important element in a power system due to following reasons:
- Fault current is higher for bus bar faults, as every feeder will contribute in fault current and bus bar impedance is very low.
- Bus bar fault may lead to outage of many feeders, depending on bus bar scheme. Mal-operation in case of out of zone fault will also cause un-necessary outage. Therefore, generally trip decision is taken after confirmation by two different components in bus bar protection.
- Non-operation of busbar protection in case of actual fault is very dangerous for equipment, persons working in system and power system itself. It will lead to delayed fault clearance and impact larger area. To avoid this redundant bus bar protection schemes are used for important installations.
- Bus bar has to compare currents of all feeders connected to it, there is requirement of all CTs having similar characteristics to avoid mal-operations in case of through faults.
- Being smaller sections, faults are considered rare for bus bars. As bus bar protection cost is higher, generally bus bar protection is not used for smaller systems.
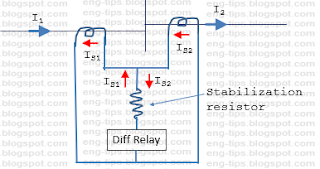
Bus bar can be considered as node, where all feeders are connected. The vector sum of all these currents shall be zero.
For understanding we may consider one bus bar with two feeders.
- It may trip for out of zone faults due to CT. Ratio error during heavy current
- Unstable due to saturation of CT magnetic circuit during heavy current
IDifferential = |I1
+ I2 + ……. In|
IBias = |I1| + |I2|
+ ……. |In|
Stability factor k = IDifferential / IBias
- Bus Bar-1 : BB Zone-1 operated and Check Zone operated
- Bus Bar-2 : BB Zone-2 operated and Check Zone operated