Introduction: Electricity is transferred on higher voltage for long distances. Transmission lines pass through forests, hills, fields etc befor reaching destination. Being exposed to uncontrolled atmosphere, faults on transmission lines are as high as 85% of the total faults in power system. These lines are protected by distance relays working on impedance function. Now with the advancement in optical fibre technology, line differential relays are also being used. Line differential relays are also having distance protection function which comes in to action whenever there is optical communication failure. In addition to protection these relays also work as fault locator which is also based on impedance measrement principle.
Line Parameters: Transmission line is a long conductor having resistance, inductance and capacitance distributed uniformly throughout the length. Following line constants are provided by designer based on calculations, which are used for relay settings:
| Sr | Parameter | Unit | |
| 1 | Positive sequence reactance | X1 | ohm/km |
| 2 | Positive sequence resistance | R1 | ohm/km |
| 3 | Zero sequence reactance | X0 | ohm/km |
| 4 | Zero sequence resistance | R0 | ohm/km |
Z secondary = Z primary x (CT Ratio / VT Ratio)
Setting calculation: We will drive settings for Station-A end relay of a 220kV line to station-B. Actual relay setting calculation will depend on many factors like relay make and model, network size etc. Here we are showing a simple example to get an idea of basics for relay setting calculation.
CT ratio: 800/1A
Primary side line parameters are:
X1 : 0.398 ohm/km
R1 : 0.069 ohm/km
X0 : 1.290 ohm/km
R0 : 0.281 ohm/km
Line length LL: 100 km
Next Longest line: 80 km
VT Ratio: 220kV/110V = 2000
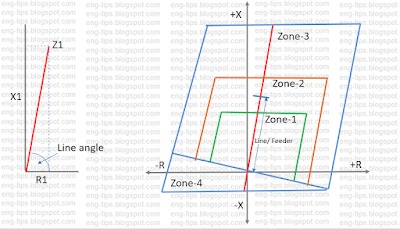
As shown in Fig-2:
Positive sequence impedance Z1 = Sqrt (R1^2 + X1^2) = 0.404 ohm/km
Line Angle = ArcTan (X1/R1) = 80.16 deg
Zero sequence impedance Z0 = Sqrt (R0^2 + X0^2) = 1.320 ohm/km
Line Angle = ArcTan (X0/R0) = 77.71 deg
Total line positive sequence impedance ZL = LL x Z1 = 40.4 ohm
Zone settings are shown in Fig-3 for a four zone protection relay. Zone-1, 2 & 3 are in forward direction and Zone-4 is in reverse direction. Typical zone settings are as below:
Zone-1: 80% of protected line = 40.04 x 0.8 = 32.320 ohm
Zone-2: 120% of protected line = 40.04 x 1.2 = 48.048 ohm
Zone-3: 100% of protected line + 120% of next longest line = 40.04 + (1.2 x 80 x 0.404) = 78.824 ohm
Zone-4: 10% of protected line = 40.04 x 0.1 = 4.04 ohm
Relay setting to be entered in relay (Secondary values):
Zone-1: Primary value x CTP/PTR = 32.320 x 800/2000 = 12.928 ohm
Zone-2: Primary value x CTP/PTR = 48.048 x 800/2000 = 19.219 ohm
Zone-3: Primary value x CTP/PTR = 78.824 x 800/2000 = 31.596 ohm
Zone-4: Primary value x CTP/PTR = 4.040 x 800/2000 = 1.616 ohm
Neutral compensation factor KZN = (Z0-Z1) / 3Z1 = 0.757
KZN Angle = ArcTan [(X0-X1)/(R0-R1)] - ArcTan (X1-R1) = -3.5 deg
Typical time settings for Zone is given below, however these are co-ordinated with relay settings of other elements of the network:
Zone-1 time delay: 0.0 sec
Zone-2 time delay: 0.5 sec
Zone-3 time delay: 1.0 sec
Zone-4 time delay: 0.5 sec